Recent Publications (Original)
Evolutionary diversification of the autophagy initiation complex: reduced Atg101 dependency and changes in Atg9 binding to Atg13
2025.09.17 Recent Publications (Original)
Zefeng Lai, Yutaro Hama, Masahide Oku, Sidi Zhang, Yasuyoshi Sakai, Hayashi Yamamoto & Noboru Mizushima*
(*責任著者)
Evolutionary diversification of the autophagy initiation complex: reduced Atg101 dependency and changes in Atg9 binding to Atg13
Autophagy. 2025 Sep 11. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2025.2559683.
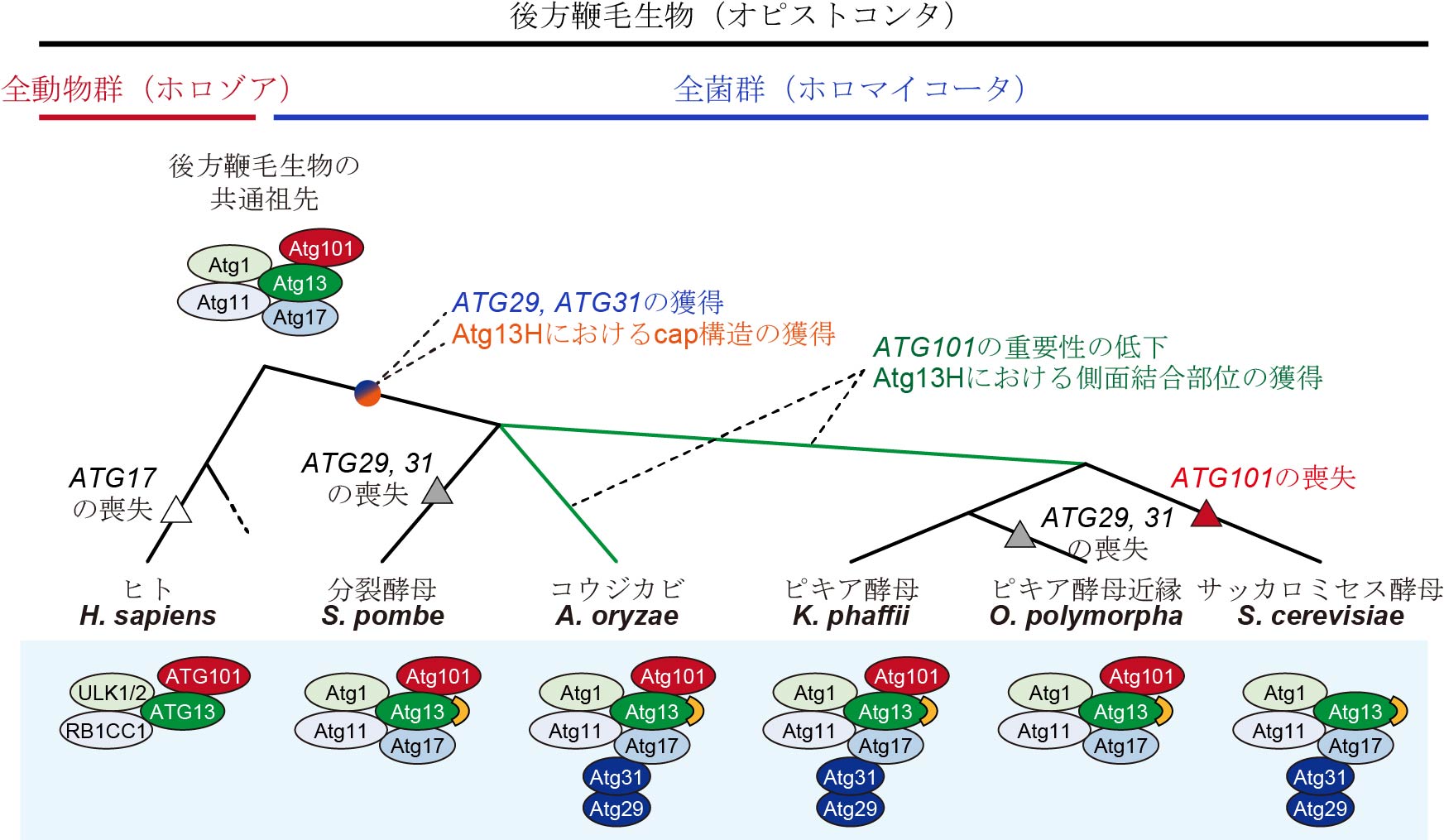
Macroautophagy/autophagy is an evolutionarily conserved process through which cells degrade cytoplasmic substances via autophagosomes. During the initiation of autophagosome formation, the ULK/Atg1 complex serves as a scaffold that recruits and regulates downstream ATG/Atg proteins and ATG9/Atg9-containing vesicles. Despite the essential role of the ULK/Atg1 complex, its components have changed during evolution; the ULK complex in mammals consists of ULK1 (or ULK2), RB1CC1, ATG13, and ATG101, whereas the Atg1 complex in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae lacks Atg101 but instead has Atg29 and Atg31 along with Atg17. In this study, we investigated how such changes have evolved. A BLAST analysis across the major eukaryotic clades revealed that ATG101, which is essential for autophagy in mammals, was lost in some Holomycota lineages after acquisition of ATG29 and ATG31 by their common ancestor. Additionally, the acquisition of a cap structure in Atg13 preceded the loss of ATG101. However, some Holomycota species have both ATG101 and ATG29-ATG31, including Aspergillus oryzae and Komagataella phaffii. Yeast two-hybrid assays showed that ATG101 is required for ATG13-ATG9 interaction in mammals but dispensable in A. oryzae, probably because of a shift in the AoAtg9-binding site in AoAtg13. We found an additive effect between atg101 and atg31 deletions in starvation-induced autophagy in K. phaffii. Furthermore, both KpAtg101 and KpAtg31 are involved in Atg1 complex assembly in K. phaffii. These findings suggest that the reduced importance of Atg101 in the Atg13-Atg9 interaction and Atg1 complex assembly enabled the eventual loss of ATG101 in some Holomycota species, including S. cerevisiae.